The post Specification in Civil Engineering appeared first on OnlineEngineeringNotes.
]]>Specification is the specific description of project which describe the nature and class of work, material to be used.
Importance of specification:
- Serves as guide for site engineers.
- Helps to clear misunderstanding and mistake of project.
- For accurate cost estimation and budgeting.
- Help to verify and check strength of material.
- Helps to meet final outcomes of project.
Purpose of specification:
- To specify nature of work.
- To estimate quantity and cost.
- To identify quantity of material.
- To identify material proportion.
- To identify type of workmanship.
Writing specification:
1. Description of material
- Provide clear description of material.
- Includes brand name and model name.
2. Workmanship
- Describe level of workmanship.
3. Tools
- Describe tools and equipment used.
- Provide rental and purchase requirement.
4. Work protection
- Instruction to protect project.
5. Expression
- Use clear and concise language.
6. Clauses of specification
- Include condition to meet work.
- Describe warranties or guarantees of work.
1.2 Specification of RCC
1. Specification material:
a. Cement:
- OPC cement is used i.e. 43 grade & IS 269:2015.
b. Coarse aggregate:
- Should hard dense and durable material like granite, basalt or limestone.
- Maximum size should exceed ¼ th of minimum thickness of member.
c. Fine aggregate:
- Should be clean free from dust, clay and organic material.
- Fineness modulus should not be more than 3.1 and less than 2.3.
d. Water:
- Clean water free from harmful impurities like oil, acid etc.
2. Combination of material:
- Should be M20 grade concrete.
- Mix proportion of cement, fine aggregate, coarse aggregate and water should be 1:1.5:3: 0.5 by weight.
- Concrete should mix mechanically using batch mixture.
3. Steel Reinforcement using IS code:
a. According IS 1786:2008, steel bar should have minimum yield strength of 415 N/mm2.
b. Steel bar should be free from rust, oil and any deleterious material.
c. As per IS 456:2000, cover should be measured from outer surface of reinforcement to surface of concrete.
d. Reinforcement should be placed as per drawing.
1.3 Specification of brick masonry
1. Specification of material:
a. Brick:
- Use 1st class brick.
- Should be in uniform shape and size.
b. Mortar:
- Should be good quality and free from lumps.
- Ratio should be (C:S:W = 1:4:0.5).
2. Combination of material:
a. Brick masonry:
- Should be laid in English bond.
b. Reinforced brick masonry:
- Should be laid in Flemish bond.
3. Steel reinforced using IS code:
- As per IS 432:1982
- Minimum diameter of steel bar = 6 mm
- Minimum cover of steel reinforcement = 15 mm
- Placed in alternative course.
- Spacing should not be more than 300 mm in horizontal and 450 mm in vertical direction.
1.4 Specification of PCC
1. Material specification:
a. Cement:
- As per IS 8112, use OPC of grade 43.
b. Coarse aggregate:
- As per IS 383, nominal size 20 mm.
c. Fine aggregate:
- Should be free from dust and organic matter.
2. Combination of material:
- W/C ratio = 0.5
- (Cement: Sand: Aggregate) = (1:1.5: 3)
3. Steel reinforcement:
- As per IS 1786
- Grade of steel should be Fe500 or Fe415
- Diameter not more than 16 mm.
- Spacing not more than 150 mm and not less than 75 mm.
- Should be free from rust and impurities.
References:
- Dutta, B.N. – Estimating and Costing in Civil Engineering, UBS Publishers, New Delhi.
- CPWD (Central Public Works Department), India – Standard Schedule of Rates and Analysis of Rates.
- IS 1200 – Indian Standard for Method of Measurement of Building and Civil Engineering Works, Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS).
- Punmia, B.C. – Estimating and Costing, Laxmi Publications.
- Building Estimation and Costing Notes – Department of Civil Engineering, Pokhara University.
- MoUD Nepal – Standard Norms and Guidelines for Public Infrastructure Development Projects.
The post Specification in Civil Engineering appeared first on OnlineEngineeringNotes.
]]>The post Valuation in Civil Engineering appeared first on OnlineEngineeringNotes.
]]>Valuation is the technique of estimating or determining the fair price or value of a property such as building, factory, other engineering structure of various types of land etc.
1.2 Purpose of valuation
- Buying or selling of property.
- For mortgage as security of loan.
- For determination of rent.
- For tax fixation or assessment of taxes.
- For compulsory acquisition.
- For fixation of insurance premium.
- To determine speculation i.e. more than fair price in selling.
- To determine betterment charges i.e. more than fair price in buying.
1.3 Terms used in valuation
1. Value and cost
- Value is the present market value of any property which may be higher or lower than cost of construction.
- Cost means actual cost of construction.
2. Book value
- It is original investment shown in account book of a company on its asset including properties and machinates.
- Book value is applicable on building and movable properties but not on land.
- Book value = Original cost – Total depreciation upto previous year
3. Assessed value
- Value of any property recorded in record of local authority which is used for the purpose of determining the various taxes to be collected from owner of the property.
4. Distressed value or forced sale value
- When a property is sold at a lower price than the market value of that time it is called distress value.
5. Replacement value
- Value of property or its services calculated on the prevailing market rate to replace the same.
6. Retable value
- Net annual letting value property which is obtained after deducting the amount of yearly repairs from gross income. Municipal and other taxes are charged on the rotable value of property.
7. Potential value
- Some property like land has an inherent value which may go on increasing due to passage of time or can fetch more return if used for some alternative purpose. This inherent value is known as potential value.
8. Annuity
- Annual periodic payment for repayment of the capital amount invested in a property or in some other form of investment by a party.
9. Perpetual annuity
- If the payment of annuity continues for indefinite period, it is known as perpetual annuity.
10. Different annuity
- If the payment if annuity begins at some future data after a number of years this is known as different annuity.
11. Scrap value
- Dismantled material value of property at the end of its utility period.
- 10% of cost of construction in case of building.
12. Salvage value
- Value of any property at the end of utility period without being dismantled.
13. Gross income
- Total income from all sources without deducting the outgoing necessary for operation, taxes, maintenance, replacements etc.
14. Outgoing
- These are the expenses incurred to maintain the property by undertaking periodic repairs.
- Also, includes government tax, sinking fund, management or collection charge other miscellaneous charges.
15. Net income
- Amount left after deducting all outgoing, operational and collection expenses from gross income. i.e. Net income = Gross income – Outgoings
16. Capitalized value
- Amount of money whose interest at the highest prevailing rate of interest will be equal to the net income from the property in perpetuity. i.e. CV = Net income * Year purchase (Y.P)
17. Years Purchase (Y.P)
- Capitalized value required to be invested in order to receive an annuity of Rs. 1 at the prevailing rate of interest. i.e. Year’s purchase = 100 / Rate of interest
18. Sinking funds
- It is a fund which is built up for sole purpose of replacement or reconstruction of a property when it loses its utility either at the end of its life span.
- S = (Sn * R)/(1+R)n-1
Where,
S = Year installment of sinking fund
Sn = Sinking fund to be accumulated in n years
R = Rate of interest
n = Utility period / Life of property
19. Depreciation
- The gradual decrease or loss in value of a property because of constant structural deterioration, use, wear and tear, decay etc.
1.4 Method of Determining value of property
1. Rental Method
- In this method the rental income is calculated after deducting all outgoing from the gross rent, years purchase is calculated after adopting the current bank interest and then capitalized value of the property is worked out.
2. Profit based Method
- Similar to rental method.
- In this method the net profit is worked out after deducting all possible outgoing and years purchase calculated after adopting current bank interest rate and multiplied by YP to get capitalized value of property.
3. Cost based Method
- In this method the actual cost incurred in constructing the building or in processing the property is taken as basis to determine the value of property.
4. Development based Method
- This method of valuation is used for properties which are in the development stage or party developed stage.
5. Depreciation Method
- Depreciated value of building is directly calculated with the help of formula
i.e. D = P [(100 – rd)/(100)]n
Where,
D = Depreciated value
P = Cost of building
rd = Rate of depreciation
n = No. of years
6. Plinth area Method
- In this method the resent plinth area rate of similar building in the same locality with the same specification is worked out, multiplied with the plinth area of building whose valuation is to be done and suitable depreciation is allowed.
7. Capital value comparison Method
- In this method, capitalized value of the property is worked out by direct comparisons with other capitalized value of similar property in the same locality, whose sale records are available.
1.5 Methods of valuation
- After doing all the valuation works the valuation report is prepared for submitting in the concerned department.
- The valuation report is divided into three parts:
- Part I: Detail about property
- Part II: Valuation calculation
- Part III: Valuation declaration
Report format:
- Cover page
- Table of content
- Valuation certificate
- Description of the property
- Appendix:
- Introductory details
- Technical details
- Area calculation
- Land value
- Land ownership certificate
- Citizenship certificate
- Drawings
- Photographs
References:
- Dutta, B.N. – Estimating and Costing in Civil Engineering, UBS Publishers, New Delhi.
- CPWD (Central Public Works Department), India – Standard Schedule of Rates and Analysis of Rates.
- IS 1200 – Indian Standard for Method of Measurement of Building and Civil Engineering Works, Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS).
- Punmia, B.C. – Estimating and Costing, Laxmi Publications.
- Building Estimation and Costing Notes – Department of Civil Engineering, Pokhara University.
- MoUD Nepal – Standard Norms and Guidelines for Public Infrastructure Development Projects.
The post Valuation in Civil Engineering appeared first on OnlineEngineeringNotes.
]]>The post Rate Analysis in Civil Engineering appeared first on OnlineEngineeringNotes.
]]>- Method of determining the rate per unit of particular item of work considering the cost and quantities of material, cost of labor, hire of tools, contractor profit etc. is known as rate analysis.
- The rate of materials and labor vary from place to place and therefore the rate of different item of work also varies from place to place.
1.2 Purpose of Rate Analysis
- To determine the actual cost per unit of item.
- To determine the economical use of material.
- To determine the cost of extra item which are not provided in contract document.
- To examine the viability of rates offered by contractor.
- To calculate the quantity of material and labor strength required for project planning.
1.3 Importance of Rate Analysis
- It gives clear picture of the various types of labor and material required for completing the particular work.
- Used to settle dispute between contractor and client.
- Used for compensation by insurance.
1.4 Requirement of Rate Analysis
- Correct information of the market rates of material.
- Correct information of the rates of various categories of labor.
- Output of labor.
- Knowledge, rate of out turn of various types plants to be used in the construction work.
- Upto date knowledge of construction work.
1.5 Factors affecting Rate Analysis
- Quality of material.
- Proportion of mortar.
- Location of site.
- Facilities available for transportation of labor and material to work site .
- Overhead charge.
- Availability of water connection.
- Possibility of theft of losses.
- Miscellaneous expenditure.
References:
- Dutta, B.N. – Estimating and Costing in Civil Engineering, UBS Publishers, New Delhi.
- CPWD (Central Public Works Department), India – Standard Schedule of Rates and Analysis of Rates.
- IS 1200 – Indian Standard for Method of Measurement of Building and Civil Engineering Works, Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS).
- Punmia, B.C. – Estimating and Costing, Laxmi Publications.
- Building Estimation and Costing Notes – Department of Civil Engineering, Pokhara University.
- MoUD Nepal – Standard Norms and Guidelines for Public Infrastructure Development Projects.
The post Rate Analysis in Civil Engineering appeared first on OnlineEngineeringNotes.
]]>The post Types of Estimates in Civil Engineering appeared first on OnlineEngineeringNotes.
]]>- Done to find out approximate cost in short time.
- This estimate is prepared after preliminary surveying.
- This estimate is prepared from practical knowledge and cost of similar works.
Types:
a. Unit rate estimate:
- In this method all cost of a unit quantity such as per km for a highway, per meter for span of bridge, per bed for hospital etc. are considered first and the estimate is prepared by multiplying the cost per corresponding unit by the number of unit of the structure.
- Buildings:
- Per student for school/college
- Per bed for hospital
- Per seat for cinema hall
- Road work:
- Per Km
- Bridge culvert:
- Per meter length
- Irrigation work:
- Per Km of canal
- Per hector of command area
b. Plinth area estimate:
- In this method, plinth area rate of building is adopted from the cost of similar building having similar specification, height and construction in same locality.
- Plinth area = Carpet area + Circulation area + Kitchen/Toilet + Wall
c. Cubic rate estimate:
- This estimate is worked out on the basis of cubical content of the proposed building and then multiplying with rate per cubic content.
- Estimate = Plinth area * height * cubical content rate
1.2 Detailed Estimate
- It is an accurate estimate which contains very detailed data about project variable such as cost/quantity and price.
- The dimension of each item are taken out correctly from drawing and quantities of each item are calculated, abstracted and billed.
- 5-10% of estimated cost for unforeseen item and 2% of work charge establishment should be added.
- This estimate is accompanied by:
- Detailed report.
- Detail specification for the execution of work.
- Detailed drawing (plans, site plan, elevation etc.)
- Calculation and design of various item such as beams, slabs etc.
- Schedule of rates followed and premium if allowed.
Factors to be considered for preparation of detail estimate:
- Quantity of materials.
- Availability of materials.
- Transportation of materials.
- Location of site.
- Availability of labor.
1.3 Revised Estimate
- It is also a detailed estimate and is prepared when the original sanctioned detail exceeds by 5%.
- Revised estimate is prepared:
- When a sanctioned estimate is likely to exceed by more than 5%.
- When the expenditure of work exceeds or is likely to exceeds by more than 10% of the administrative approval.
- When there is material rate deviation from original proposal.
- When sanction estimate is more than actual requirement.
1.4 Supplementary Estimate
It is also a detailed estimate and is prepared when additional work is required to supplement the original work.
1.5 Annual repair and maintenance estimate
In order to keep the structure in proper condition annual repair and maintenance are carried out. The estimate prepared for this purpose is known as annual repair and maintenance estimate.
1.6 Extension and improvement estimate
When some changes and extension are required to be made in the old work, a detailed estimate of extension and improvement work is carried out which is called as extension and improvement estimate.
1.7 Complete Estimate
- In complete estimate following should be included:
- Cost of land.
- Cost of preliminary work.
- Cost of preliminary design, drawing and estimate.
- Cost of detailed design, estimate, specification and contract documents.
- Cost of electricity, water supply and sanitary work.
- Cost of design and supervision charges
- Cost of external service.
- Cost of repair and maintenance.
1.8 Split up of cost and building work
a. General split up:
- Labor cost = 30-35% of total cost
- Material cost = 65-70% of total cost
b. Stage wise breakup:
- Construction below plinth level = 10-15% of total cost
- Construction above plinth level = 85-90% of total cost
c. Activity wise breakup:
- Foundation work = 17-18%
- Brickwork/block work = 20%
- Concreting and reinforcement steel = 15%
- Door, windows and ventilation = 12%
- Roof water proofing & finishing = 5%
- Plastering = 5-6%
- Flooring = 5%
- Painting = 2-3%
- Water supply and sanitation = 12-13%
- Other work = 4-5%
References:
- Dutta, B.N. – Estimating and Costing in Civil Engineering, UBS Publishers, New Delhi.
- CPWD (Central Public Works Department), India – Standard Schedule of Rates and Analysis of Rates.
- IS 1200 – Indian Standard for Method of Measurement of Building and Civil Engineering Works, Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS).
- Punmia, B.C. – Estimating and Costing, Laxmi Publications.
- Building Estimation and Costing Notes – Department of Civil Engineering, Pokhara University.
- MoUD Nepal – Standard Norms and Guidelines for Public Infrastructure Development Projects.
The post Types of Estimates in Civil Engineering appeared first on OnlineEngineeringNotes.
]]>The post Foundation Soil Improvement Methods appeared first on OnlineEngineeringNotes.
]]>Foundation soil improvement:
- Process of improving engineering properties of soil to make more stable foundation.
- Reduce permeability and compressibility of soil.
- Increase shear strength of soil.
- Increase bearing capacity of foundation of soil.
Method of soil improvement:
- Mechanical compaction
- Dynamic compaction
- Soil stabilization by use of admixture
- Sand compaction piles
- Soil stabilization by injection of suitable grout
1.2 Mechanical compaction
- It is the process of increasing density of soil by application of mechanical energy.
- For cohesive soil compaction is done till optimum moisture content.
- For cohesion less soil compaction is done by vibrating.
Purpose:
- Increase shear strength.
- Reduce compressibility.
- Reduce permeability.
Equipment:
1. Smooth wheeled roller
2. Vibratory roller
3. Impact rammer
1.3 Preloading
- Soil improvement by applying compressive load to reduce settlement and increase bearing capacity.
- It is also known as tempory loading.
1.4 Sand compaction pile and stone column
Sand compaction pile:
- This method is used for improving ground stability, preventing liquefaction and reducing settlement.
- Process: By installing sand into soft ground by casting pipe and vibrating the sand to produce firmly compacted sand piles in the ground.
Stone column:
- This method is used for installing and compacting pile to reduce liquefaction.
- Size of stone are 6 mm to 40 mm.
1.5 Soil stabilization by the use of admixture
- Physical properties of soil can be improved economically by use of admixture like lime, portland cement and asphalt.
- Applicable only in shallow foundation.
Types of admixture:
1. Soil cement admixture
- Mixture of cement and water with soil and compacted to high density.
- PPC cement is used.
- Used in sub base and base course on road.
2. Soil lime stabilization
- Improves strength, stiffness and density.
- Reduce plasticity index.
- Used in canal lining.
1.6 Soil stabilization by injection of suitable grout
- It is the process by which fluid like material either in suspension or in solution is injected in void space of underground soil or rock.
Effective in following case:
- When foundation has to be constructed below ground water table.
- Difficult for access of foundation level.
- Geometric dimension of foundation is complicated.
Types of soil stabilization by injection of suitable grout:
- Chemical grouting ( silica and resins)
- Cement grouting
References:
- Terzaghi, Karl, Peck, R.B & John, Wiley (1969) Soil mechanics in engineering practice, New York.
- Arora , K.R (2008), Soil mechanics and foundation engineering, Delhi: Standard Publisher Distribution.
The post Foundation Soil Improvement Methods appeared first on OnlineEngineeringNotes.
]]>The post Well Foundation Types and Construction appeared first on OnlineEngineeringNotes.
]]>- Deep foundation provided below water level.
- Also known as caissons foundation.
- Used for bridge construction.
Types of well foundation
1. Open well
- Both top and bottom are open during construction.
- Cost is cheap.
- Rate of progress is slow.
2. Pneumatic caissons
- Open at bottom and closed at top.
- Sunk vertically.
- Construction cost is quite high.
3. Box caissons
- Open at top and closed at bottom.
- Cost of construction is low.
Shape of well foundation
1. Circular well
- Commonly used shape.
- Maximum diameter is 9 m.
2. Doub D-well
- Sunk easily.
- Used for pier.
3. Double octagonal well
- Shape of well is better than double D-well.
4. Twin circular well
- Two indepent wall.
- Small depth of sinking.
5. Rectangular wall
- Used for bridge foundation.
- Large foundation, double rectangular well.
1.2 Component of well foundation
- Well cap: Transmit load of super structure to steining.
- Steining: Transmit load to subsoil.
- Well curb: Facilitates process of sinking.
- Cutting edge: Cuts soil during sinking.
- Bottom plug: Transmit load to sub soil.
- Dredge hole: Hole formed during excavation.
- Top plug: Concrete plug constructed at top.
1.3 Depth of well foundation
- Depth is dependent on:
1. Minimum grip length below scour depth.
2. Base pressure to be within permissible load.
- Normal depth of scour is calculated by lacy’s formula.
d = 0.473 (Q/f)1/2
Where,
Q = Design discharge in cumecs
f = Lacy’s factor = 1.76m1/2
d = Scour depth
m = mean particle size
- Regime width of water way (W)
W = CQ1/2
Where,
W = Regime width
C = Constant
- Actual water way length (L) is less than regime width.
- The actual depth(d|) = d(W/L)0.67
- Grip length: Depth of bottom of well below maximum scour level.
1.4 Force acting on well foundation
- Live load: Load is not constant and change with time.
- Impact load: Sudden load.
- Wind load: Horizontal load.
- Force due to water.
- Seismic force.
- Earth pressure.
1.5 Construction and sinking of well
1. Sinking of a well
Steps:
a. Laying of curb
- If river bed is dry the cutting edge is placed.
- If water table is upt 5 m sand is land is created.
- If water table is more than 5 m more economical curb is built.
b. Construction of well steining
- Steining is constructed with a height of 1.5 m at time of sinking.
c. Sinking operation
- Material is excavated mechanically or manually. Manual work can be done upto 1 m height.
- Well os allowed to remain vertical.
- Sinking in well increase skin friction.
2. Tilt and shift of well
- Objective is to well sunk should sunk straight and vertical.
Cause of tilt and shift:
- No – uniform bearing capacity.
- Obstraction on one side.
- Unequal removal of soil.
Precausion:
- Uniform thickness cutting edge should be provided.
- Tilt and shift should be carefully noted.
Remedial measure of tilt and shift:
1. Control dredging
- Done more on higher side.
2. Eccentric loading
- Provide greater sinking effort on higher side of wall.
3. Pushing the wall
- Applied on lower side of wall.
4. Pulling the wall
- Applied on higher side of wall.
5. Water jetting
- Used for outer face of higher side.
References:
- Terzaghi, Karl, Peck, R.B & John, Wiley (1969) Soil mechanics in engineering practice, New York.
- Arora , K.R (2008), Soil mechanics and foundation engineering, Delhi: Standard Publisher Distribution.
The post Well Foundation Types and Construction appeared first on OnlineEngineeringNotes.
]]>The post Lateral Earth Pressure Theories appeared first on OnlineEngineeringNotes.
]]>Lateral earth pressure:
- The pressure exerted by soil in horizontal direction.
Lateral earth pressure = K * over burden stress
or, σh = K* σv
or, σh = K* γZ
where,
K = Coefficient of lateral pressure
Types of lateral earth pressure:
1. Earth pressure at rest
- When soil mass is not subjected any lateral yielding or movement the pressure in this condition is known as earth pressure at rest.
2. Active earth pressure
- Occurs when soil mass yields in such a way that it tends to stretch horizontally.
- It is the state of plastic equilibrium as the entire soil mass is on verge of failure.
3. Passive earth pressure
- When retaining wall moves inward to the backfill the soil gets compressed and failure due to upward movement of wedge occurs.
1.2 Rankine’s earth pressure theory for active and passive state
Rankine’s earth pressure theory:
Assumption
- Soil is homogenous and semi-infinite.
- Back of retaining wall is vertical and smooth.
- Ground surface is plane which may be horizontal or inclined.
- Soil is dry and cohesion less.
- Wall movement is sufficient so that plastic equilibrium is fulfilled.
Rakine’s various backfill condition are:
A. Rankine theory for cohesionless soil (C=0)
1. Rankine theory for horizontal backfill
a. Active earth pressure
Consider,
- σv = γZ
- Intially there is no lateral movement.
i.e σh = Ko* σv
- As the wall moves away from the soil σv remains same but σh decreases till failure occurs i.e σh → σa.
As wall moves away
σa = Ka σv
Now, for expression of Ka
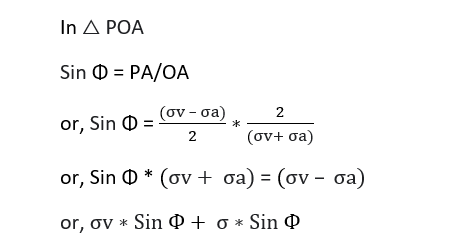
References:
- Terzaghi, Karl, Peck, R.B & John, Wiley (1969) Soil mechanics in engineering practice, New York.
- Arora , K.R (2008), Soil mechanics and foundation engineering, Delhi: Standard Publisher Distribution.
The post Lateral Earth Pressure Theories appeared first on OnlineEngineeringNotes.
]]>