1.1 Definition and type of earth pressure
Lateral earth pressure:
- The pressure exerted by soil in horizontal direction.
Lateral earth pressure = K * over burden stress
or, σh = K* σv
or, σh = K* γZ
where,
K = Coefficient of lateral pressure
Types of lateral earth pressure:
1. Earth pressure at rest
- When soil mass is not subjected any lateral yielding or movement the pressure in this condition is known as earth pressure at rest.
2. Active earth pressure
- Occurs when soil mass yields in such a way that it tends to stretch horizontally.
- It is the state of plastic equilibrium as the entire soil mass is on verge of failure.
3. Passive earth pressure
- When retaining wall moves inward to the backfill the soil gets compressed and failure due to upward movement of wedge occurs.
1.2 Rankine’s earth pressure theory for active and passive state
Rankine’s earth pressure theory:
Assumption
- Soil is homogenous and semi-infinite.
- Back of retaining wall is vertical and smooth.
- Ground surface is plane which may be horizontal or inclined.
- Soil is dry and cohesion less.
- Wall movement is sufficient so that plastic equilibrium is fulfilled.
Rakine’s various backfill condition are:
A. Rankine theory for cohesionless soil (C=0)
1. Rankine theory for horizontal backfill
a. Active earth pressure
Consider,
- σv = γZ
- Intially there is no lateral movement.
i.e σh = Ko* σv
- As the wall moves away from the soil σv remains same but σh decreases till failure occurs i.e σh → σa.
As wall moves away
σa = Ka σv
Now, for expression of Ka
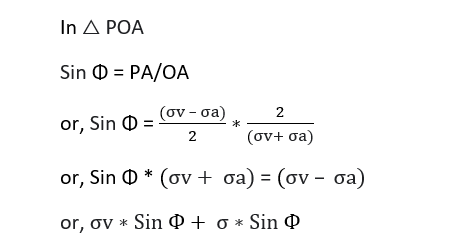
References:
- Terzaghi, Karl, Peck, R.B & John, Wiley (1969) Soil mechanics in engineering practice, New York.
- Arora , K.R (2008), Soil mechanics and foundation engineering, Delhi: Standard Publisher Distribution.