1.1 General layout of components in a typical storage power plant
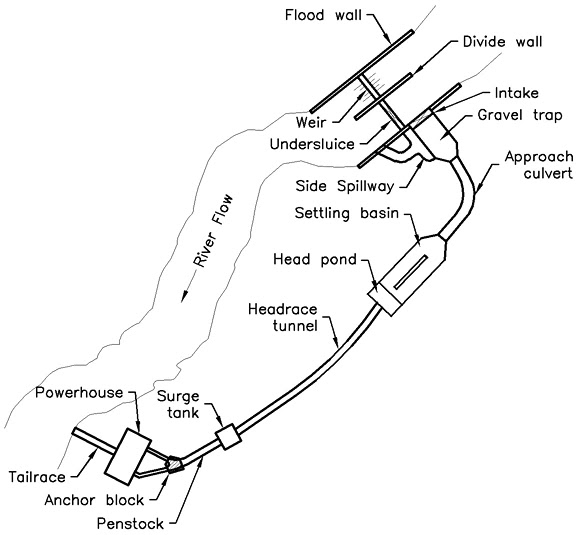
1.Dam:
- A barrier built across a river to control the flow of the water.
2. Reservoir:
- An artificial lake created by a dam to store water for future use.
3.Intake:
- A structure for diverting water from a river or lake into a canal or pipeline.
4.Spilway:
- A structure that allows excess water from a reservoir to be released safely.
5.Tunnel:
- A underground passage for conveying water from one place to another.
6.Surge tank:
- A tank that is used to absorb sudden increases in pressure in a water system.
7. Penstock:
- A pipe or conduit used to carry water from a reservoir to a turbine.
8. Power house:
- A building where electricity is generated from hydropower.
9. Tailrace canal:
- A canal or other waterway used to divert the water discharged from a turbine back into a river or lake.
1.2 Dams and their appurtenant works
Classification of dam:
a.Based on function:
1.Storage dam:
- Constructed to store water for drinking and hydropower.
2.Diversion dam:
- For diversion of flow of river.
3. Detention dam:
- To reduce the flood peak discharge.
4. Debris dam:
- Constructed to reduce slope of channel.
5. Coffer dam:
- Temporary structure used to keep water out of an area.
b.Based an material:
- Concrete dam
- Earthen dam
- Masonry dam
- Timber dam
- Steel dam
- Rock fill dam
c.Based on mode of structural load transfer:
1. Gravity dam:
- A large structure made of concrete or masonry that uses weight to resist the force of water.
2. Arch dam:
- It is a curved structure made of concrete or masonry the relies on the shape of the dam to resist the force of water.
3.Buttress dam:
- It is a structure made of concrete or masonry that uses support of column or buttresses to resist the force of water.
Forces acting dams and their combination:
1. Primary load:
- Self-weight load
- Water load
- Uplift pressure
2. Secondary load:
- Silt load
- Wave load
3. Exceptional load:
- Earthquake load
- Hydrodynamic wave load
Site selection for dams and selection of type of dam:
Site selection for dam:
1.Topographical factor:
- Dam is suitable at neck of river valley where river is narrow and valley has large storage capacity.
2.Geological factor:
- If the foundation consist of sound rock any type of dam can be constructed on it.
- Rock like granite and schist make satisfactory foundation for gravity dam.
- Poor rocks and gravel foundation are suitable for earth dam and rock fill dam.
- If the foundation is not so strong but abutment are good to takeup thrust then arc dam is taken.
3. Accessibility:
- Dam site should be easily accessible.
- It economize the transportation cost of construction materials, equipment and manpower.
4.Sociological factor:
- The social impact of building a dam must also be carefully considered. Local communities may be affected in many ways, including displacement, access to resources and employment opportunities.
5.Availability of resource:
- The availability of resources such as land, water and labor must be considered when selecting a dam site. Without adequate resources, building a dam is impossible.
Selection types of dams:
- Identify the purpose of the dam.
- Examine the site condition.
- Determine the site of dam.
- Cost of dam.
- Environmental impact.
Principle variant of embankment and concrete dam:
| Concrete dam | Embankment dam |
| These require sound and stable rock. | These are suitable for almost all type of foundation. |
| Costlier to build. | Cheaper to build. |
| Longer construction period. | Shorter construction period. |
| More stable and durable. | Less stable and durable. |
| Low risk of overtopping. | Higher risk of overtopping. |
| Constructed with concrete and steel. | Constructed with earth, rocks and other material. |
Failure mode:
Failure modes of embankment and their prevention:
1.Slope failure:
- Slope failure occurs when the embankment is constructed on a weak foundation or when the soil has a low shear strength.
Prevention:
- Conduct proper subsurface investigation to determine the foundation condition.
- Provide drainage to reduce pore pressure.
2. Seepage failure:
- It occurs when water is able to penetrate the embankment and erode the foundation or cause instability.
Prevention:
- Use proper compaction technique.
- Install a filter layer or cut off wall to prevent seepage.
3.Settlemetn failure:
- It occurs when the embankment is constructed on low bearing capacity soil.
Prevention:
- Conduct a proper subsurface investigation to determine the foundation condition.
Failure modes of concrete dam and their prevention measures:
1. Seepage failure:
- Common failure in concrete dam.
- It occurs when water escapes through the concrete either due to cracks or joints in the dam structure.
Prevention:
- Installing water proof membrane.
- Ensuring sufficient concrete mix.
2.Overtopping failure:
- It occurs when the water level rises above the top of the dam.
Prevention:
- Design dam with spillway or emergency gate to allow excess water to release safely.
- Construct dam to the correct height.
3.Structure instability:
- It occurs due to inadequate foundation or poor design.
Prevention:
- Performing geotechnical investigation.
4.Earthquake:
- It can cause significant damage to concrete dam leading to failure.
Prevention:
- Design the dam to withstand earthquake using seismic dampers and reinforcing structure.
Foundation treatment:
- It is the process of treating the soil under and around a structure’s foundation to prevent water and moisture from damaging this structure.
- It includes waterproof membranes, drainage system and soil stabilization method.
Grouting:
- It is the process of filling voids, cracks and joint in rocks and soil with a cementitious material to provide a watertight seal and increase the strength of foundation.
Middle third rule:
- It suggest a channel to be designed such that the water depth is equal to one-third of the channel width.
- The rule helps ensure the turbine is placed in an optimal position to optimize efficiency.
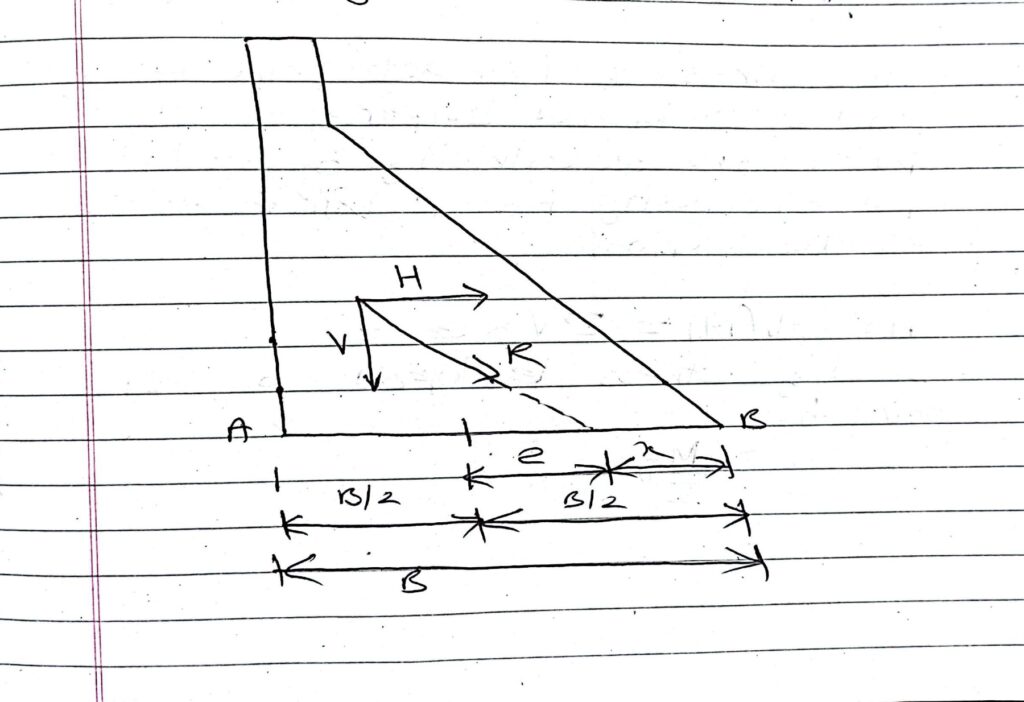
Stress analysis in concrete dam:



Gates:
- Gates are the structure that are used to regulate the flow.
- Provide additional storage on the dam during dry season.
Types of gate:
1.Vertical lift gate:
- Used to raise and lower the water level or a river and reservoir.
2. Radial gate:
- Simple and most reliable and cheap.
- Used to regulate the flow of water in reservoir or conduit.
3.Flap gate:
- Normally operates at partially open condition.
- Consist of number of flaps that are hinged together and can be opened or closed in order to control the flow of water.
4.Stop log gates:
- Used in low head hydropower.
- Consist of number of wooden or metal plank that move up and down to control amount of water.
5.Flash board:
- Used only in small spillway.
- Consist of wooden board or panel hinged at the bottom and support by struct.
1.3 Reservoir sedimentation issues and sedimentation management in brief
Reservoir sedimentation:
- It is the accumulation of sediment in a reservoir over time due to natural or human caused process.
- Sedimentation can reduce the storage capacity of the reservoir and decrease the efficiency of hydroelectric power plant.
Sedimentation management:
- Design and construct sediment basin to trap and store sediment.
- Improve water management.
- Monitor and measure sediment load.
- Constructing dam in stages.
- Installing sediment removing equipment.
- Utilizing environmentally friendly sediment management technique.
References:
- Dandekar, M. M., & Sharma, K. N. (2010). Water Power Engineering. Vikas Publishing House.
- Punmia, B. C., Pande, B. B. L., Jain, A. K., & Jain, A. K. (2016). Irrigation and Water Power Engineering. Laxmi Publications.
- Singh, Bharat (2018). Fundamentals of Hydrology and Hydropower Engineering. Nem Chand & Bros.
- Central Water Commission, Government of India (2019). Handbook on Hydroelectric Engineering.
- International Energy Agency (IEA) (2021). Hydropower Status Report. Retrieved from www.iea.org
- Nepal Electricity Authority (NEA) (2022). Annual Report on Hydropower Projects in Nepal. Retrieved from www.nea.org.np
- United States Bureau of Reclamation (2020). Design of Small Dams. U.S. Government Printing Office.

