1.1 Introduction to quality control/assurance
| Quality control | Quality assurance |
| Monitoring and inspecting the final product. | Ensuring quality throughout the entire process. |
| Identify and improve defect. | Prevent the defect. |
| Limited to final product. | Covers entire production control. |
| Improves final products quality. | Ensure consistent quality in production. |
| Testing car brakes before delivery. | Ensure manufacturing process meets specification. |
1.2 Objective of QC/QA
- Compliance with standards: Ensure products meet established standard and specification.
- Defect prevention: Identify and rectify defects to improve products quality.
- Customer satisfaction: Deliver products meet customer expectation.
- Cost control: Minimize expenses.
- Risk mitigation: Reduce chances of project failure.
1.3 Factors affecting quality of construction
- Design
- Material selection
- Workmanship
- Weather condition
- Equipment condition
- Site management
- Regulations
1.4 Quality control technique
- Inspection: Detailed examination to identify defects.
- Testing: Evaluating products performance standards.
- Statical process control (SPC): Monitoring using data.
- Root cause analysis: Identifying underlying issues.
- Lean construction: Reducing waste to enhance quality.
1.5 Preparing QC plans
- Preparing QC plan: Developing plan to ensure quality standard are met.
- Approval of material source: Verifying supplies and source meet quality criteria.
- Material sampling: Collecting representative samples for testing.
- On-site laboratory testing: Testing material using an on site lab for immediate results.
- Off-site laboratory testing: Sending samples to external labs for in-depth analysis.
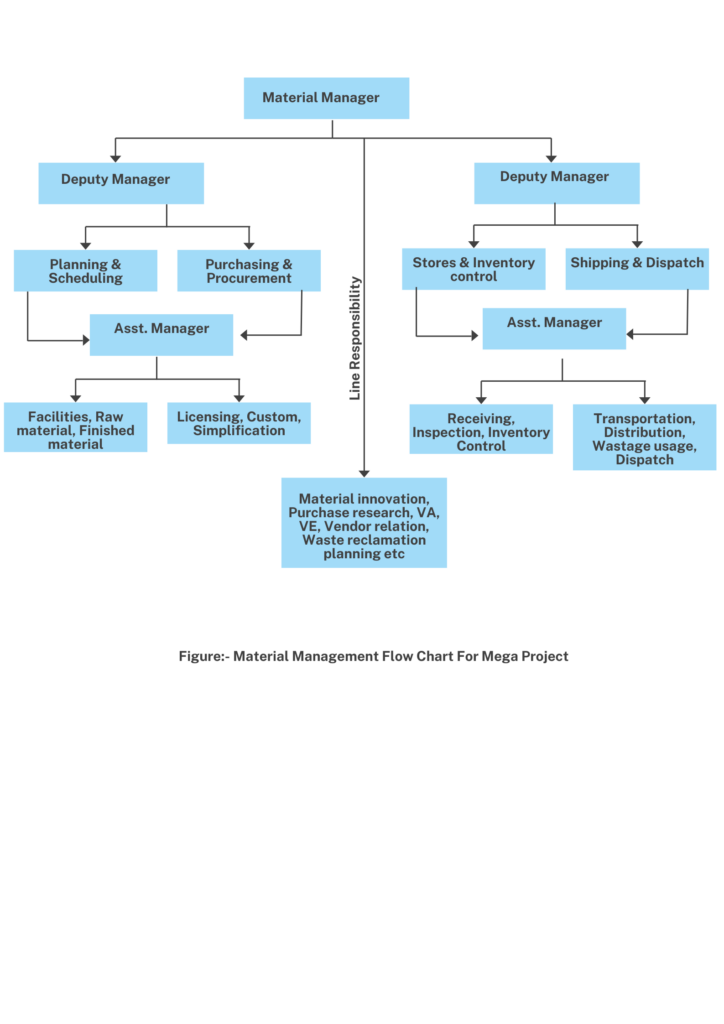
1.6 Material Management
- Material management involves planning, storing, distributing and controlling materials used in construction project to ensure efficient usage, minimize waste and meet project goal.
Importance:
- Minimize wastage
- Quality control
- Risk reduction
- Budget control
- Client satisfaction
Purchase management:
- Project of acquiring goods and services needed for a project.
- Ensure timely availability of required material.
- Establish relationship with reliable suppliers.
Inventory management:
- Involves tracking and controlling the stock of materials, components and product to ensure adequate supply while minimizing shortage.
- Prevent shortage.
- Maintain transparency.
Construction garbage:
- Waste generated during construction activities.
- Minimize environment impact through waste management.
Surplus material:
- Excess materials or left over after construction which may not be used for project.
Material management flow chart for mega project
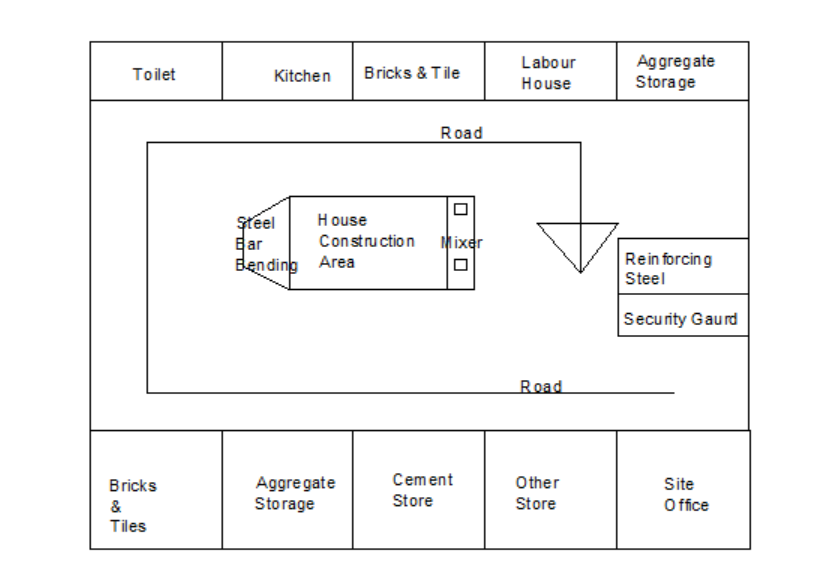
Factors affecting construction site planning:
- Site condition: Terrain, soil type and environmental factors.
- Access: Availability of road and transportation.
- Utilities: Access of water, electricity.
- Safety: Measure of worker safety.
- Cost: Budget influence site design and layout.
- Project scope: Nature and size of construction project.
- Project schedule: Timeline and sequencing activities.
Sample of site layout plan:
Reference:
• Harold Kerzner (2017). Project Management: A Systems Approach to Planning, Scheduling, and Controlling.
• PMI (2021). A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide) – 7th Edition.
• Nebosh, Nepal Engineering Council Syllabus (2024). Engineering Professional Practice Notes.
• Civil Engineering Standard Method of Measurement (CESMM).
• Personal Class Notes & Presentations from Nepalese Engineering Institutions.

