1.1 Definition of soil and rock
Soil are the uncemented aggregate of mineral and decayed organic matter containing liquid and gas in the empty space of solid particles.
Types of soil :
- Residual soil:
A soil is said to be residual if it is formed by disintegration of rocks without transportation.
- Transported soil:
A soil is said to be transported by disintegration of rocks with the action of transfortation medium like air, water etc.
Rock is the natural occuring solid substance that are formed by minerals.
1.2 Formation process of soil :
Rock-soil cycle or Rock-soil interaction:
- It is an interaction between rock and soil.
- Soil is formed due to disintegration of rock.

Disintegration of rocks:
There are two types of disintegration of rocks:
- Physical Disintegration :
Formation of cohesion less soil and sand.
- Temperature change:
Change in temperature causes expansion and contraction of rocks and hence cracks occurs.
- Wedging action of rocks:
The wedging action of ice causes expansion of rocks and hence disintegration occurs.
- Spreading of roots of plants:
It causes cracking in rocks and hence disintegration occur.
- Abrasion:
Due to air, water and glacier wear and tear of rock occurs and hence disintegration occur.
2. Chemical decomposition:
Formation of cohesive soil and clay.
- Hydration:
Rock in contact with water causes hydrolysis and hence change in volume occur.
- Carbonation:
CO2 + H2O → H2CO3 ( Carbonic acid)
Carbonic acid in contact with rock causes disintegration.
- Oxidation:
Oxygen ion in contact with rock minerals causes decomposition.
- Solution:
The submerged rock causes expansion and hence decomposition.
1.3 Definition of soil mechanics and its importance in civil engineering:
Soil mechanics is the branch of science that deals with the physical properties of soil and the behaviour of soil masses subjected to various types of forces.
Importance of soil mechanics in civil engineering:
- Foundation:
Foundations are required to transmit load of the structure to soil, safely and efficiently without the shear failure and excessive settlement of soil mass.

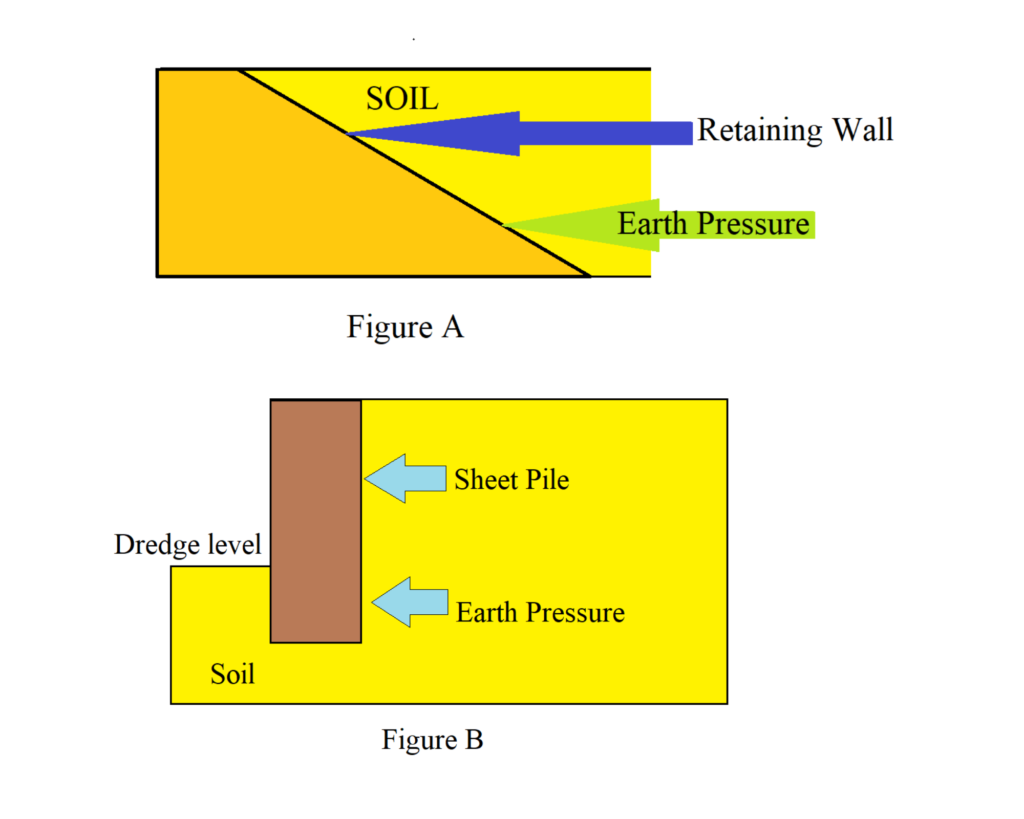
- Retaining structures:
When sufficient space is not available for the mass of soil to spread and to form a safe structure it is required to retain the soil. Soil engineering gives the theories of earth pressure on retaining structure.
- Stability of slopes:
If soil surface is not horizontal then there is a component of weight of soil which tends to move downward and causes instability of slope. Hence, soil engineering provides the methods for checking stability of slopes.

- Underground structure:
It helps to design and construct the underground structures such as tunnels, shafts, conduits etc.

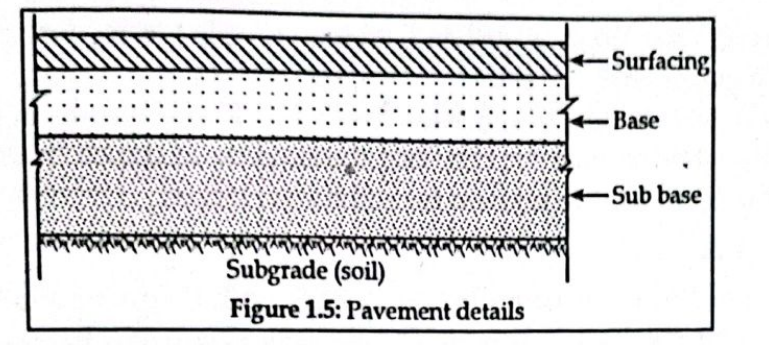
- Pavement design:
A pavement is a hard crust provied on soil for the purpose of a smooth and strong surface on which vechicles can move. Soil mechanics gives the idea about design of pavement.
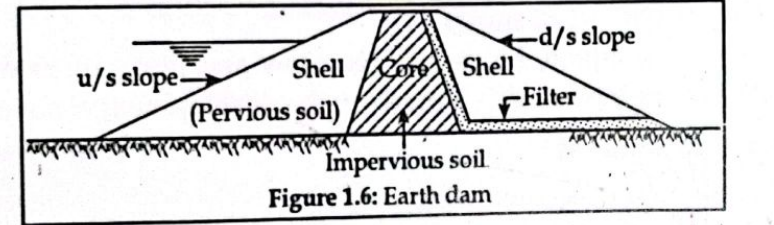
- Earth dam:
Earth dam are huge structure in which soil is used as a construction material. The earth dam are built for creating water reservoirs. Extrem care must be taken while constructing earth dam because the failure of eath dam may lead huge disaster.
- Miscellaneous soil problem:
Miscellaneous soil problem related to soil such as soil heave, soil subsidence, frost heave, shrinkage and swelling of soil etc. has to be tackled by geotechnical engineer during constrution phase. Soil mechanis gives the idea about these problems.
References:
- Terzaghi, Karl, Peck, R.B & John, Wiley (1969) Soil mechanics in engineering practice, New York.
- Arora , K.R (2008), Soil mechanics and foundation engineering, Delhi: Standard Publisher Distribution.

