1.1 Exploration and development of groundwater:
Exploration of groundwater:
- Objective is to locate aquifier capable of yielding water of suitable quality, for irrigation, drinking water, agricultural and industrail purpose.
- Done by geophysical drilling.
Methods:
1. Surface exploration:
- Geological method.
- Remote sensing.
- Surface geophysical method.
2. Sub- surface exploration:
- Test drilling.
- Geophysical logging.
Aquifer:
- Aquifer is underground water bearing layer of permeable rock.
- Types:
a. Confined aquifer: Presence of underground water.
b. Unconfined aquifer: Open to atmospher.
- Advantage of ground water:
- Less investment required.
- No channel required.
1.2 Types of well:
- Well are vertical holes driven below the ground surface to extract water from ground.
a. Shallow well:
- Hole which has been dug, bored, driven or drilled into ground for purpose of extracting water.
b. Deep well:
- Well drilled to an aquifer below an impervious strata.
- Water is hard and contains dissolved salt.
1.3 Components of tube well:
- A tube well consist of 100 to 200 mm wide stainless steel tube or pipe which is bored into underground aquifer.
Components:
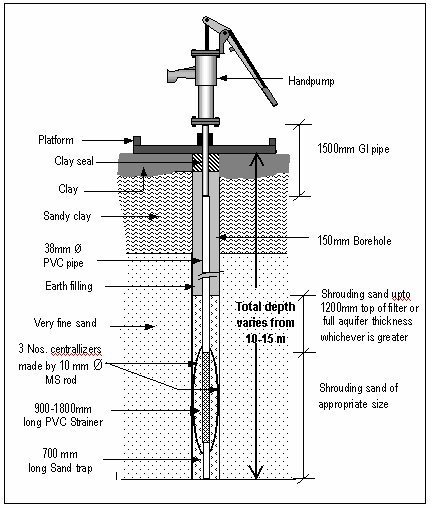
a. Temporary reservoir:
- Small reservoir of water made at outlet of tube well.
b. Casing:
- Support to the well.
- Protect borehole from collapse.
c. Screening:
- Help to maintain good water supply from aquifer.
- Allow for long term satisfactory operation of well.
1.4 Design consideration of shallow and deep well:
- Determining location of well.
- Water well design and installation.
- Well drilling.
- Well development (includes well screen, well casing is developed and borehole is cleaned).
- Well head protection (construction of well seal and use of backflow prevention device).
1.5 Type and selection of pump:
Types of pump:
1. Centrifugal pump:
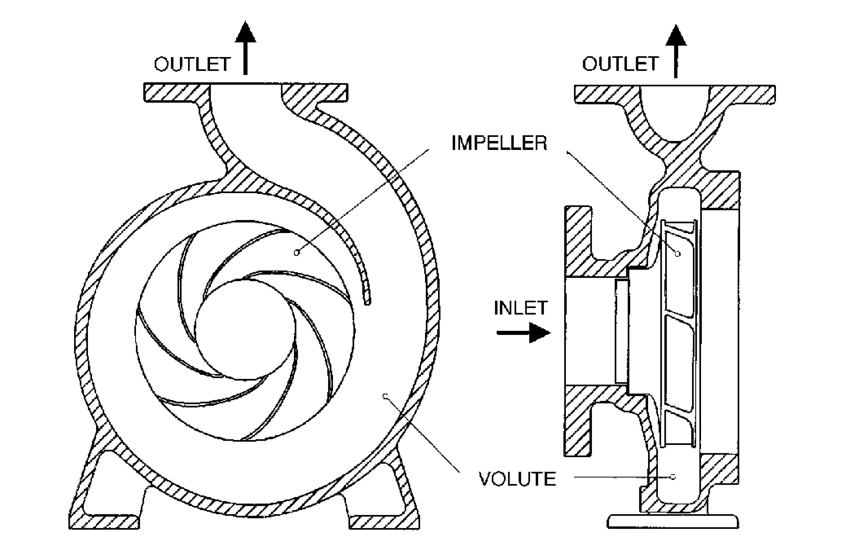
- Mechanical device designed to move a fluid by means of transfer of rotational energy from one or more driven rotors called impeller.
- Simple design and produce high flow rate and high efficiency.
2. Reciprocating pump:
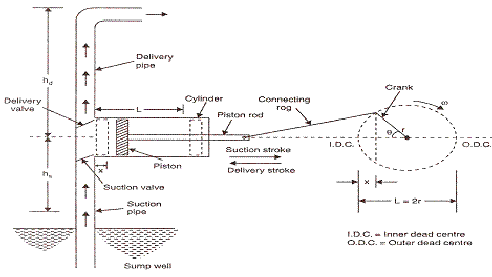
- Pump which uses backward and forward movement to move a fluid.
- Provide steady, unchanging flow rate.
- Better than centrifugal pump.
Selection of pump:
- Should be capable of pumping required quantity of water.
- Intial cost should be cheap.
- Maintenance cost should be cheap.
- Should be reliable.
- Should be high efficeient.
- Should have long life and depreciation cost should be small.
- Cost of labour should be low.
1.6 Conveyance and distribution system in ground water irrigation schemes:
- Water is conveyed from ground water source to cropped field using network of open channel or pipe line.
- Pipe line have more advantage than open channel because it save water and energy consumption.
- Though underground pipe distribution system is expensive it have many advantage such as:
- Farmers receive water near the field.
- Seepage, evaporation loss are avoided.
- Quantity of water delivered is same in each outlet.
- Maintenance cost is low.
- Full control of water supply.
1.7 Conjunctive use of surface and ground water:
- Conjuctive use is the combined use of surface water and ground water resource in a unified way to optimize water use and minimize adverse effect of using a single source.
- Efficient and ecnomic way to maximize agricultural production.
Advantage:
- Problem of water logging is reduced.
- Promotes sustainable water management.
- Improves environmental condition of irrigated area.
- Enhance water use efficiency.
Limitation:
- Reduce pump efficiency due to large fluctuation of water level.
- Active participation of people required for proper conduction.
- Construction of ground water recharge structure required.
References:
- WECS (1998), Design Guidelines for Surface Irrigation in Terai and Hills of Nepal, (Vol. I and II)
- Michael, A.M.(2011). Irrigation theory and practice
- FAO(1977). Guidelines for Predicting Crop Water Requirements. FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper No. 24.

