1.1 Purpose, importance and types of foundation
Purpose / Importance:
- To determine the type of foundation.
- To determine design parameter for the foundation such bearing capacity and allowable soil bearing pressure.
- To calculate potential settlement of foundation.
- To determine expansion potential at the site.
- To investigate the stability of slope and their effect on adjacent structure.
- To investigate possible way of improving the soil to increase the foundation bearing capacity.
Types of foundation:
A. Shallow foundation
- Width greater than its depth.
- Located just below the lower part of wall or column which it support.
Types of shallow foundation:
1. Strip / Continuous footing
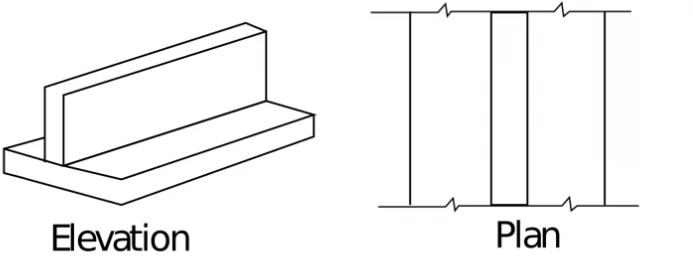
- Provided for load bearing wall.
- L>B.
2. Spread / Isolated footing
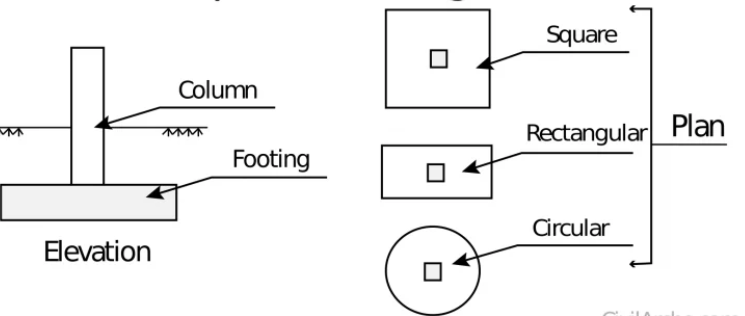
- Circular, square or rectangular slab of uniform thickness.
3. Combined footing
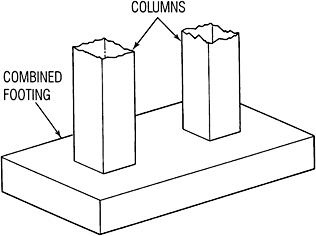
- Supports two or more columns in row.
- Preferred in limited space.
4. Strap / Cantilever footing
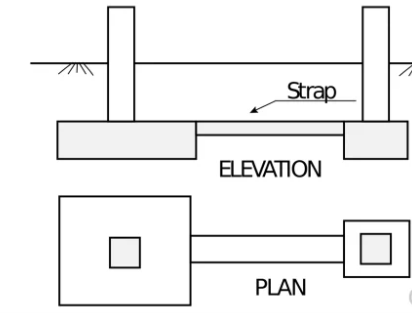
- Two or more footing connected by beam.
5. Mat / Raft foundation
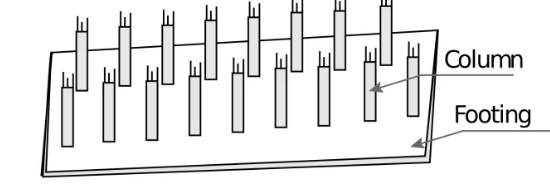
- Consist of large slab supporting number of column and walls.
B. Deep foundation
- Depth is greater than width.
- Distributes load from super-structure vertically rather than laterally.
Types of deep foundation:
1. Pile foundation
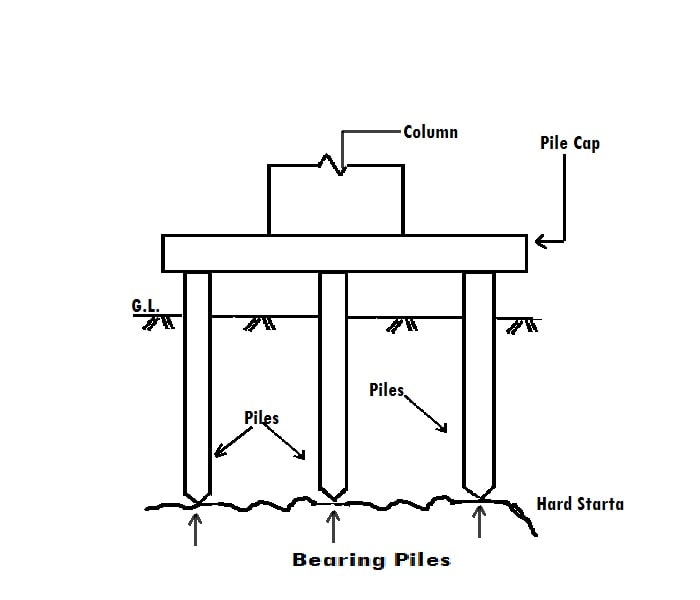
- Column made of wood, steel, concrete of RCC.
- Embedded into the ground to transmit the load of the structure to a hard stratum or compressed soil.
2. Pier foundation
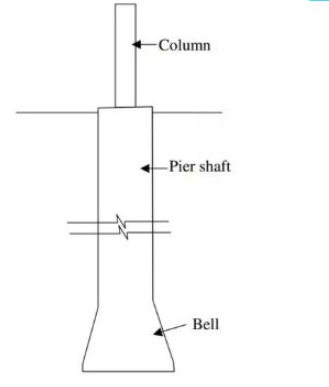
- A cast insitu pile greater than 0.6 m diameter is termed as pier.
- Consists of cylindrical column of large diameter to support and transfer load.
3. Well foundation
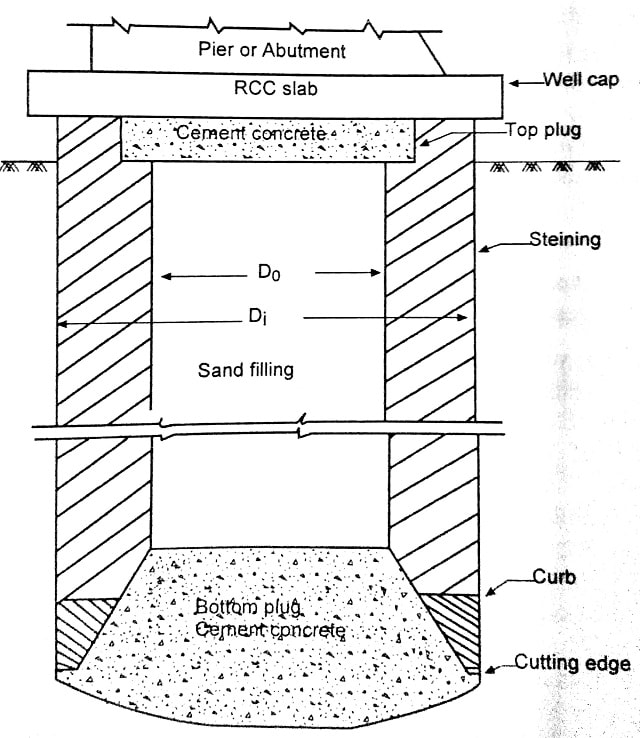
- Well is a type of cassion.
- Suitable for soil containing large boulders.
1.2 Factors affecting choice of foundation
- Function of structure.
- Cost of foundation.
- Sub-surface condition of soil.
- Boundry criteria.
- Bearing capacity of soil.
- Types of load of super structure and other load acting on foundation.
1.3 Introduction to machine foundation
- Foundation provided below the super strucutre of a vibrating and rotating machine for installation is called machine foundation.
- Includes the studies of vibration of foundation soil system transmitted by wave energy.
- Used for supporting turbines, large electric motor and generator.
- Wave energy transmitted through the underlined soil from the foundation should not cause harmful effects to machine, structure of people.
1.4 Types of machine foundation
1. Block foundation
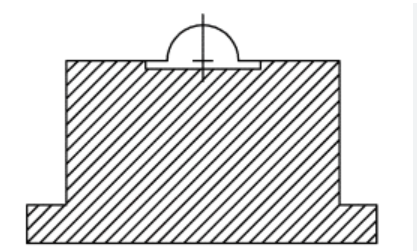
- Consists of a pedestal resting on a footing.
- It has large mass and smaller natural frequency.
- Provided for compressor and reciprocating engine.
2. Box or caisson’s foundation
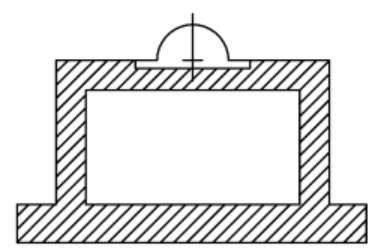
- Use for lighter foundation.
- It has smaller mass and higher natural frequency.
3. Wall type foundation
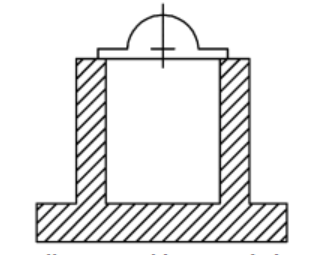
- Consist of well-column and beam slab.
- Steam turbines are provided with wall type foundation.
1.5 Types of machine
1. High speed machine
- Turbo generator and rotary compressor fall in this category.
- Speed ranging from 3000 to 10000 rpm.
2. Low speed machine
- Compressor and reciprocating engine comes in this category.
- Speed is smaller than 600 rpm.
3. Impact type machine
- Produce impact loading.
- Speed is usually 60 to 150 blows per minute.
References:
- Terzaghi, Karl and peck, R.B. John Wiley.(1967). Soil mechanics in engineering practice, New York.
- Arora K.R. (1997). Soil Mechanics and foundation engineering, India: Standard Publisher Distribution.

